Abstract
Hypertension, as soon as considered a ailment of older populations, is more and more everyday among young
adults in low- and center-income international locations, consisting of Pakistan. This paper explores the
epidemiology, hazard factors, socio-monetary implications, and public health challenges of hypertension
in young Pakistani patients aged 15–forty. The findings propose an pressing want for preventive strategies,
centered cognizance campaigns, and systematic screening, particularly in urban and semi-urban
populations.
Introduction
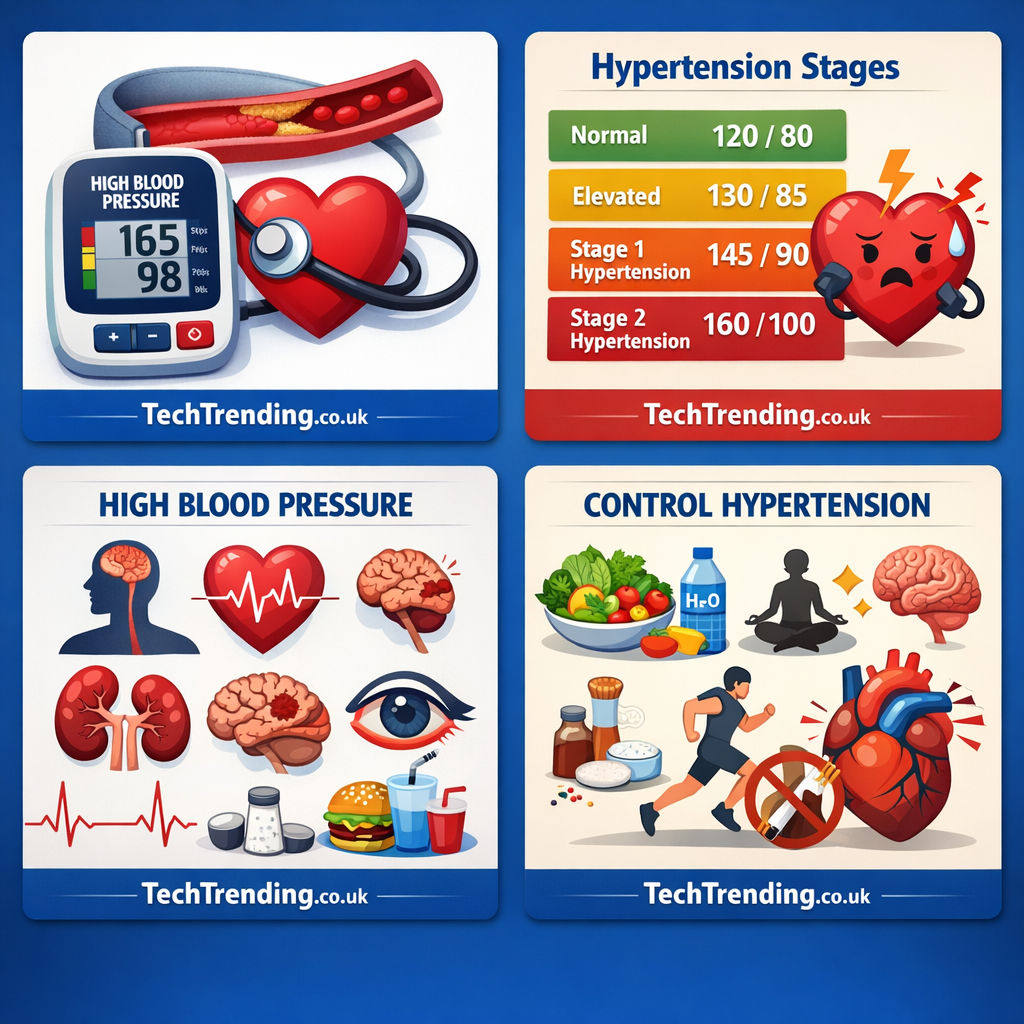
Hypertension is a major modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disorder, which stays the leading purpose of dying globally. Even as historically related to older adults, evidence increasingly more suggests that young people, which includes teenagers and adults below 40, are growing hypertension at alarming prices. In Pakistan, a country with a young populace—in which over 60% are under the age of 30—the developing occurrence of high blood pressure among teens presents a significant public health challenge.
Epidemiology
Latest research from tertiary hospitals and community health surveys in Pakistan have proven that
between 12% and 25% of teenagers aged 15–forty are both pre-hypertensive or hypertensive. Urban
areas, such as Karachi, Lahore, and Islamabad, report a better incidence than rural areas. Male
patients tend to be more affected than ladies on this age organization, despite the fact that the gender hole narrows
appreciably inside the past due 20s and early 30s.
Risk Factors
3.1 Way of Life Sedentary behavior:
The rapid urbanization and digitalization of exertions and entertainment have contributed to decreased physical interest stages.
Nutritional conduct: Excessive salt consumption, low fruit and vegetable consumption, and extended rapid meals
intake make contributions substantially.
Weight problems: Pakistan has one of the highest fees of youth and younger grownup obesity in South Asia.
3.2 Psychosocial Factors
Strain: Instructional pressures, unemployment, and societal expectations are related with expanded stress,
which increases blood strain.
Smoking and substance use: Using tobacco products, inclusive of shisha and smokeless tobacco, is
common among younger men.
3.3 Environmental and Genetic Factors
South Asian populations, which include Pakistanis, have a robust familial predisposition to high blood pressure. Environmental pollutants and restricted get right of entry to to green regions further exacerbate the circumstance.
Diagnosis and Awareness
There is low cognizance and early detection of high blood pressure in younger people in Pakistan. A observe
conducted in Punjab in 2023 located that only 30% of hypertensive teens have been aware of their
situation, and less than 10% had it below control. Many instances are located simplest when headaches
rise up, inclusive of complications, vision issues, or signs and symptoms of organ damage.
Public Health Challenges
5.1 Inadequate Screening
Routine screening isn’t generally practiced in primary care, mainly for people below 40, until symptomatic.
5.2 Health System Limitations
Preventive care integration is constrained, primary care services are overburdened, and the healthcare device lacks trained employees.
5.3 Socioeconomic Barriers
Low-income populations face worrying conditions in having access to care, affording medicinal drug, and adopting
way of existence changes. There’s moreover cultural stigma round chronic infection in young adults.
Interventions and Policy Recommendations
6.1 National Screening Programs
Enforce habitual blood strain screenings in faculties, colleges, and places of work.
6.2 Health Education
youngsters-unique public campaigns on food plan, exercise, and quitting smoking incorporation of hypertension
training modules into faculty curriculums.
6.3 Digital Health Tools
Cellular packages and SMS reminders must help track and control blood strain in more youthful users.
6.4 Regulatory Measures
Taxes on excessive-salt processed meals and better labeling guidelines.rules proscribing the sale of tobacco to underage people.
Conclusion
High blood pressure in younger sufferers in Pakistan represents a silent however developing epidemic. Early
identification and prevention techniques are important to mitigate prolonged-term cardiovascular risks. Multisectoral collaboration—along with authorities our our bodies, instructional institutions, healthcare
companies, and community corporations—is vital to deal with the basis reasons and enhance outcomes
for the u . s .’s adolescents.
References
(Be aware: You may request whole citations or a reference list in APA, MLA, or any preferred style.)WHO (2023). Global reputation file on Noncommunicable diseases.
Pakistan high blood pressure League opinions, 2022–2024.
Jafar, T. H. et al. (2020). Occurrence and threat elements for hypertension in Pakistan: A national
pass-sectional look at. The Lancet neighborhood fitness. National Health Survey of Pakistan (2023).